Different layouts of Highway
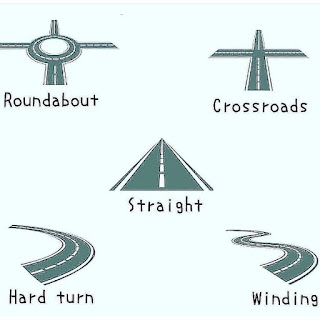
In highway and road design and terminology, the terms you've mentioned typically refer to different types of road alignments or configurations. Here's how they are generally classified: Roundabout: A roundabout is a type of circular intersection or junction where traffic flows in one direction around a central island. It is designed to improve traffic flow, reduce congestion, and enhance safety compared to traditional intersections with traffic signals or stop signs. Crossroad: A crossroad refers to an intersection where two roads cross each other at approximately right angles (90 degrees). Crossroads are common in urban and rural areas and typically have traffic signals, stop signs, or yield signs to control traffic flow. Straight Road: A straight road is a linear roadway segment that runs in a continuous straight line without significant curves or bends. Straight roads are common in highway design, especially in flat terrain where the landscape allows for minimal horizontal...


